PID控制C源程序
2013-04-03
标签:
PID
PID控制C源程序,可以参考一下
struct _pid {
int pv; /*integer that contains the process value*/
int sp; /*integer that contains the set point*/
float integral;
float pgain;
float igain;
float dgain;
int deadband;
int last_error;
};
struct _pid warm, *pid;
int process_point, set_point, dead_band;
float p_gain, i_gain, d_gain, integral_val, new_integ;;
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------
pid_init
DESCRIPTION This function initializes the pointers in the _pid structure
to the process variable and the setpoint. *pv and *sp are
integer pointers.
------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void pid_init(struct _pid *warm, int process_point, int set_point)
{
struct _pid *pid;
pid = warm;
pid->pv = process_point;
pid->sp = set_point;
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------
pid_tune
DESCRIPTION Sets the proportional gain (p_gain), integral gain (i_gain),
derivitive gain (d_gain), and the dead band (dead_band) of
a pid control structure _pid.
------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void pid_tune(struct _pid *pid, float p_gain, float i_gain, float d_gain, int dead_band)
{
pid->pgain = p_gain;
pid->igain = i_gain;
pid->dgain = d_gain;
pid->deadband = dead_band;
pid->integral = integral_val;
pid->last_error = 0;
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------
pid_setinteg
DESCRIPTION Set a new value for the integral term of the pid equation.
This is useful for setting the initial output of the
pid controller at start up.
------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void pid_setinteg(struct _pid *pid, float new_integ)
{
pid->integral = new_integ;
pid->last_error = 0;
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------
pid_bumpless
DESCRIPTION Bumpless transfer algorithim. When suddenly changing
setpoints, or when restarting the PID equation after an
extended pause, the derivative of the equation can cause
a bump in the controller output. This function will help
smooth out that bump. The process value in *pv should
be the updated just before this function is used.
------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
void pid_bumpless(struct _pid *pid)
{
pid->last_error = (pid->sp) - (pid->pv);
}
/*------------------------------------------------------------------------
pid_calc
DESCRIPTION Performs PID calculations for the _pid structure *a.
This function uses the positional form of the pid equation,
and incorporates an integral windup prevention algorithim. Rectangular integration is used,
so this function must be repeated on a consistent time basis for accurate control.
RETURN VALUE The new output value for the pid loop.
USAGE #include "control.h"*/
float pid_calc(struct _pid *pid)
{
int err;
float pterm, dterm, result, ferror;
err = (pid->sp) - (pid->pv);
if (abs(err) > pid->deadband) {
ferror = (float) err; /*do integer to float conversion only once*/
pterm = pid->pgain * ferror;
if (pterm > 100 || pterm < -100) {
pid->integral = 0.0;
}
else {
pid->integral += pid->igain * ferror;
if (pid->integral > 100.0) {
pid->integral = 100.0;
}
else if (pid->integral < 0.0) {
pid->integral = 0.0;
}
}
dterm = ((float)(err - pid->last_error)) * pid->dgain;
result = pterm + pid->integral + dterm;
}
else {
result = pid->integral;
}
pid->last_error = err;
return (result);
}
void main(void)
{
float display_value;
int count = 0;
pid = &warm;
// printf("Enter the values of Process point, Set point, P gain, I gain, D gain \n");
// scanf("%d%d%f%f%f", &process_point, &set_point, &p_gain, &i_gain, &d_gain);
process_point = 30;
set_point = 40;
p_gain = (float)(5.2);
i_gain = (float)(0.77);
d_gain = (float)(0.18);
dead_band = 2;
integral_val = (float)(0.01);
printf("The values of Process point, Set point, P gain, I gain, D gain \n");
printf(" %6d %6d %4f %4f %4f\n", process_point, set_point, p_gain, i_gain, d_gain);
printf("Enter the values of Process point\n");
while (count <= 20) {
scanf("%d", &process_point);
pid_init(&warm, process_point, set_point);
pid_tune(&warm, p_gain, i_gain, d_gain, dead_band);
pid_setinteg(&warm, 0.0); //pid_setinteg(&warm,30.0);
//Get input value for process point
pid_bumpless(&warm);
// how to display output
display_value = pid_calc(&warm);
printf("%f\n", display_value);
//printf("\n%f%f%f%f",warm.pv,warm.sp,warm.igain,warm.dgain);
count++;
}
}
可能会用到的工具/仪表
相关文章
推荐文章
-
一款高温报警电路2024年11月13日 81
-
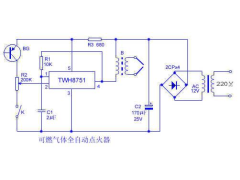
可燃气体全自动点火器2012年09月22日 76
-
LED参数与特性2012年09月18日 118
-
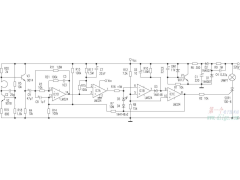
RC振荡电路的几种接法2012年09月10日 221
-
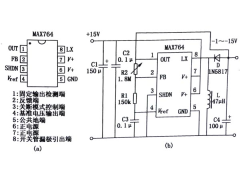
MAX764极性反转电路2012年08月24日 47
-
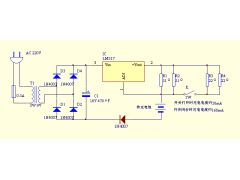
实用恒流充电器2012年08月18日 175
-
电子催眠器制作2012年08月15日 72
-
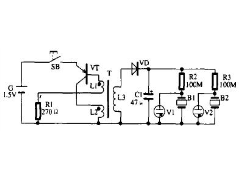
多普勒自动电子开关2012年08月02日 78
热门文章
-
常用物质金属非金属的电阻率、导电率明细表2024年11月23日 4875
-
自制微型交流电焊机2012年07月14日 1143
-
声光控延时开关的制作2024年07月06日 915
-
用LM1875替找TDA20302012年09月15日 777
-
6N3+LM4780功放制作2012年09月13日 653
-
小型太阳能供电板的制作2012年09月08日 649
-
简单的逆变器电路2012年07月08日 560
-
1000米晶体稳频FM立体声发射机2012年07月22日 499
章节目录